Taxonomies, Ontologies, Semantic Models & Knowledge Graphs
Several people have recently asked me about taxonomies, ontologies, and semantic models and why they are important. In this blog post, I hope to show you why these are foundational steps to Knowledge Graphs, and by extension, to AI/ML solutions.
Taxonomies
A taxonomy is a hierarchical framework, or schema, for the organization of organisms, inanimate objects, events, and/or concepts. We see taxonomies daily as humans, and we don’t give them much thought. Taxonomies are the facets, filters, and search suggestions commonly seen on modern websites.
For example, books can be categorized as fiction and nonfiction at a high level. That may work in some instances, but in most cases, that is too high of a grouping level, so we further subdivide each high-level category until we are satisfied we have achieved an appropriate grouping level. Figure 1 shows an example of a taxonomy for books.
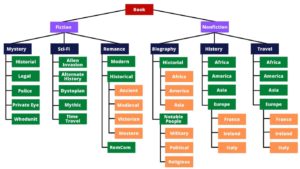
Figure 1. – Book Taxonomy
Another taxonomy example is how you sort your documents on your computer. For example, some may choose to start with a subject and then sub-divide by year, while others may do the opposite.
There are no absolute right and wrong with taxonomies, just degrees of appropriateness. The most important question to ask when creating a taxonomy is, “does this hierarchical grouping meet my needs?”
Ontologies
According to Wikipedia, an ontology “encompasses a representation, formal naming, and definition of the categories, properties, and relations between the concepts, data, and entities that substantiate one, many, or all domains of discourse.” In other words, ontologies allow us to organize the jargon of a subject area into a controlled vocabulary, thereby decreasing complexity and confusion. Without ontologies, you have no frame of reference, and understanding is lost. As Robert Engles states in his blog post On the role and the whatabouts of Ontology, ontologies are “essential in modern architectural patterns to ensure data quality, governance, findability, interoperability, accessibility, and reusability.”
For example, an ontology will allow one to associate the Book taxonomy with the Customer taxonomy via relationships.
An ontology is more challenging to create than a taxonomy because it needs to capture the interrelationships between business objects/concepts by encapsulating the language and terminology of the business area you are modeling.

Figure 2. – OntologiesStephen DeAngelis, Ontology Power of Understanding
A properly created ontology will expose the understanding of how the elements in the model relate to each other. Based on this understanding, one can infer intent via the relationships. A virtual assistant like Alexa uses these relationships phrases and synonyms of those phrases to define the user’s intention.
Semantic Data Model
A Semantic Data Model is a method of organizing data that reflects the basic meaning of data items and the relationships among them. An example of a semantic model is a conceptual data model. This model has enough information to convey meaning to someone who may not know or understand the subject area.
We call semantic models to contain the ontology and the factual knowledge in a large, combined model with definitions added to concepts, links, and facts based on business needs.
Knowledge Graphs
Knowledge graphs are models that instantiate the taxonomy and ontology via a semantic model using the actual data and associated relationships. These graphs are the foundation for us to realize the promise of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) capabilities by capturing and exposing the relationships between nodes. These relationships contain data and metadata about the relationship between nodes, which is very different from the inferred relationships between columns of data in a relational database.
This relationship data and metadata is critical to successful Machine Learning (ML) solutions. By creating an understanding of the relationships between the nodes, we can achieve progressive improvements to the improvement of the data model without creating and injecting new code. These incremental improvements to the knowledge graph are critical to implementing Artificial Intelligence (AI) because this mimics how the human brain can reassess a concept or situation based on new data and derive a course correction.
AI/ML solutions like this already exist and are used every day. Fraud detection solutions, virtual assistant tools like Alexa, Netflix recommendations, and the “someone you may know” features on Facebook or LinkedIn use AI/ML, built on taxonomies, ontologies, and semantic data models.
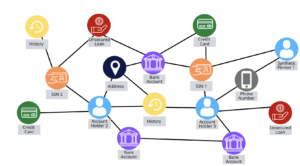
Figure 3. – Fraud Detection Knowledge Graph
In conclusion, don’t try to skip steps. Instead, start any AI/ML solution by ensuring you have laid a good foundation of understanding via taxonomies and ontologies that will create a robust and flexible knowledge graph.
About the Author
Jim McHugh is the Vice President of National Intelligence Service – Emerging Markets Portfolio. Jim is responsible for the delivery of Analytics and Data Management to the Intelligence Community.

