Leveraging Taxonomies, Ontologies, & Semantic Models

A few months ago, I published a blog titled Taxonomies, Ontologies, Semantic Models & Knowledge Graphs, and the response was tremendous. I had no idea that so many people were interested in metadata management. Because of this response, I thought I would dive deeper into this topic and provide greater detail on how to leverage your metadata better.
Taxonomies are hierarchical frameworks, or schemas, for the organization of organisms, inanimate objects, events, and/or concepts. In other words, taxonomies are containers used to classify people, places, or things. We see taxonomies everywhere, from science (domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genius, and species) to the grocery store (bakery, dairy/eggs, frozen food, meat, produce, snacks, etc.) to the faceted navigation within most of today’s web properties.
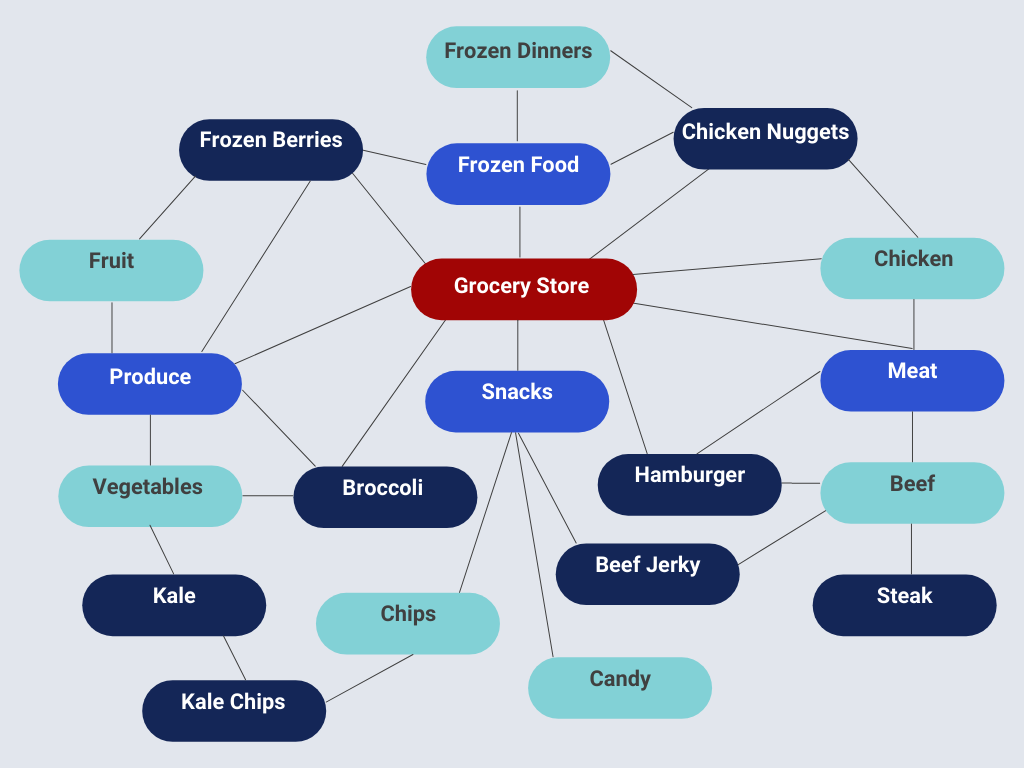
On the other hand, ontologies are formal naming and definition of the categories, properties, and relations between the concepts, data, and entities. Ontologies provide specificity about the taxonomy by providing a controlled vocabulary. Tom Gruber, who founded Siri, presented the idea that ontologies were “an explicit specification of a conceptualization.” [1]
Gruber asserted that ontologies must adhere to five design criteria. First, an ontology must be clear and objective, “effectively communicating the intended meaning of the defined term.” Second, the ontology must also be coherent, logically and consistently applying the definition to the concept. Third, he stated that an ontology is a conceptual foundation upon which one can extend the ontology for future use of the shared vocabulary. Fourth, the ontology must also contain minimal encoding bias and eliminate the incorporation of implementation decisions within the ontology. Finally, Gruber states that “an ontology should require the minimal ontological commitment sufficient to support the intended knowledge sharing activities,” thereby allowing the users of the ontology the freedom to customize the ontology as required.
The next logical step was taking the knowledge representation captured by the ontology and extending it into a semantic model. Parsing and deconstructing the spoken and written word into understandable computer commands leverages an ontology, providing a powerful way to automate the collection and transformation of data into actionable information.
Semantic Models are a conceptual visualization of how objects and their corresponding data relate to other objects. These models create a non-technical way to understand the data supporting both application development and data analytics.
By converting the ontology to a semantic model, you can now fully harness the power of your data by automating these low-level, error-prone tasks to computers. This automation frees up the time for Data Analysts to focus on their mission and strategic decision-making instead of extracting, cleaning, and loading raw data into their Decision Support System (DSS). Instead, the analysts can focus on strategically interpreting this high-speed, high-fidelity information. Now armed with better situational awareness based on timely and highly accurate information, the Data Analyst implements an appropriate response.
This information can also be simultaneously run against existing models at the speed of thought to ensure the analyst implements the correct course of action. If there is a divergence between the analyst’s response and the computer-generated response based on the models, the decision can be routed to an expert for a final decision.
The power of properly generated ontologies and semantic models to help make better decisions is priceless from the financial sector to the defense sector.
References
[1] Thomas R. Gruber, Toward principles for the design of ontologies used for knowledge sharing?, International Journal of Human-Computer Studies, Volume 43, Issues 5-6, 1995, Pages 907-928, ISSN 1071-5819
About the Author
Jim McHugh is the Vice President of National Intelligence Service – Emerging Markets Portfolio. Jim is responsible for the delivery of Analytics and Data Management to the Intelligence Community.

